Prototyping: The Pros and Cons of Low Fidelity vs. High Fidelity Design
Many designers become confused about choosing low-fidelity and high-fidelity. However, both have some unique features. It’s all about context and priorities when deciding between high and low fidelity. High-fidelity and low-fidelity prototyping are not replacements for one another, and employing both at different points in the development process is typically recommended.
To clarify your confusion, we will explain what you need to know about prototypes. It will help you determine the difference between low-fidelity and high-fidelity design prototypes.
A Brief Explanation of Prototypes
Knowing the prototypes’ definitions is essential before discussing low-fidelity and high-fidelity design prototypes. Why should you need it in web design?
So, a software prototype is an early form of the final result used for evaluation before it is released to the public. It is used to test fundamental ideas and procedures. Moreover, prototypes are a standard feature of the process of design. Users and other stakeholders provide feedback on their ideas through these methods. That feedback helps them make their design more user-friendly and better. By doing so, they may be able to save time and money on a project. Otherwise, they may fail before it has even begun development.
So, whenever we are asked to describe the significance of prototyping quickly, we always respond by stating that it assists us in the following ways:
- Concentrate on crucial design components.
- Identify any gaps in functionality early on, and you may iterate at a lesser price.
- Extend the lifespan of your product.
There is a common misunderstanding that prototypes are the same as static wireframes and mockups. But that’s not like that. Prototypes replicate interactions and user flows via clickable objects added to wireframes and mockups.
Now we’ll move to our next section, where we explain two significant types of prototypes. They are low-fidelity prototypes and high-fidelity prototypes. But first, let’s define fidelity and see why it’s so crucial.
What Does Fidelity Mean In UX Design?
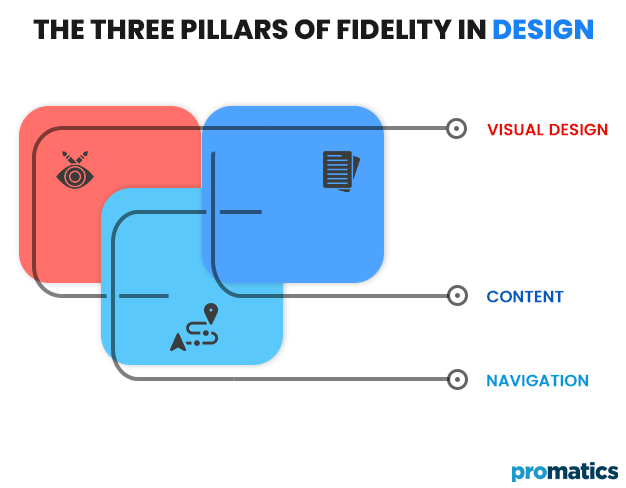
When discussing prototypes, “fidelity” describes how well a model represents the final product. It may also explain the prototype’s degree of detail and functionality. The degree of fidelity may differ in the following areas:
- Visual design
- Content
- Navigation
Paper and sticky notes might suffice for specific prototypes since they require little interaction. Other prototypes, however, are shown digitally with elaborate interaction and navigation elements. Prototypes range from paper to digital and everything in between, defining their category. The two primary subtypes fall under this category:
- Low-Fidelity Prototype
- High-Fidelity Prototype
Before beginning to design prototypes, you must know how much time and effort you can put into the project. To that aim, you may create either low- or high-fidelity prototypes.
Low-Fidelity Prototype
Prototyping at a low-fidelity (lo-fi) level efficiently turns abstract design ideas into tangible objects that can be physically inspected and evaluated. The primary aim of lo-fi prototypes is to test and validate the product’s functioning, not its aesthetics.
This prototype lets you test, evaluate, and gather feedback in the early phases of app development by turning your ideas into actual objects. Or you can use it to identify the design issues during the brainstorming phase of UX design. So where can you use this prototype?
You can take eCommerce checkout flow as an example of a low-fidelity prototype.
An instance for completing a purchase might look like this:
Home page > product page > cart > checkout > confirmation > thank you.
How to Create Low-Fidelity Wire Frames?
Wireframes that are simple to alter and keep up to date may create with the help of low-fidelity wireframing tools like Figma or Invision. It can help you make more polished prototypes to showcase your ideas.
It’s easy to make low-fidelity wireframes using this tool if you follow the instructions.
- List the essential features you want to include in your design. In this list, you can add tabbed sections, content sections, and associated control according to your need.
- We’ll create prototypes of those elements in the next phase. You can create mockups on paper or in photoshop. These mockups help you to evaluate their compatibility and identify areas for improvement.
- In the third section, you can add some notes to the wireframes. Thus, your consumer comprehends your work.
Now a question may pop into your mind, what types of elements should you include in your low-fidelity wireframe that make your design easier to evaluate and improve?
- You may use text for buttons, menus, and other UI elements. This text will help your client to understand every element’s functionality.
- Add vector images for buttons and menus as background images.
- Lastly, include non-textual items like photos, which may be readily identified as supplementary images later in development.
Best Examples of Low-Fidelity Wireframes
Now, you are searching for the most excellent low-fidelity websites. Below are some examples:
Mobile Site with a Low-Quality Home Page
This homepage wireframe design considers content placement without specifying the content. In the center of the design, you can put a play button that indicates an embedded video. This example shows how to organize your components, not where to place them.
QC Low-Fidelity Wireframes
If you want to test your sign-in page or pricing page design, you can use these wireframes. It covers all the essential features of logging in, resetting your password, and what the price page looks like.
Portfolio Website
Your user interface design portfolio should balance personality, usefulness, and information. So you can use low-fidelity websites to display your work and case studies in an attractive and easy-to-understand manner.
The Reasons for Using Low-Fidelity Wireframes
After observing these examples, you must understand why low-fidelity wireframes are used. Here are the reasons:
i.) You can test your designs before developing your UI design.
ii.) Next, you can send your initial design to your clients so you can get feedback on that. It’ll help you develop your design or guide you through adding new things if needed.
iii.) You can quickly revise and change your design with low-fidelity wireframes.
iv.) Low-fidelity wireframes demonstrate a website or app’s appearance without content. It lets you easily share site information with customers, stakeholders, and coworkers.
It’s essential to know when should you need to use it. You can use it in the initial stage of your UI design. You can also help test your user flow, ensure everything works, and design. It also reduces prototype costs. Getting feedback from your users without paying too much will be more convenient.
High-Fidelity Prototype
High-fidelity prototypes are similar to the finished product in look and performance. These prototypes are practical, dynamic, and comprehensive. For example, touching an image/button will simulate a genuine product’s look, feel, and navigation. Hi-fi prototypes are commonly used in the final step before coding to evaluate usability and workflow concerns with actual users and stakeholders.
For example, if you’re making an iOS app, you’ll want to take advantage of the iPhone 14 Pro’s frame, which measures 393 by 852. High-fidelity wireframes provide accurate measurements for every UI element.
Moreover, Wireframes with high fidelity is made with actual or realistic text. You should compose the texts or contact the team’s content manager if you have none. If the wording you wish to use is not final, don’t panic; it can be changed.
How to create High-Fidelity Prototypes?
Several online and offline tools, packed with essential features, may be used to develop an attractive design. It has several tools that will help you build an appealing design and layout in just a few hours.
Templates:
These integrated features allow the new user to make changes and create an appealing prototype.
Cloud-based software:
You can now access your project across all your devices and keep it in sync no matter where you are.
Interactive prototyping:
Create interactions and animations by adding gestures of different types to your prototype.
a.) First, visit your online or offline tools and create your account. Then, decide what kind of gadget and project you want to do.
b.) In this step, you must create a project for high fidelity wireframe and enter your desired widgets.
c.) Then, add those widgets to your “My Widget” for future use.
d.) Choose widgets and tap “Add Link” on the screen panel on the right to add links. Afterward, configure the widget’s action, target, gesture, screen, and animation.
e.) You can create a “Create Master” by clicking on your widgets. You can save it to the master library.
f.) You may also use the “Sticky” feature in the widget library to permanently attach the notes to the widgets. After choosing Sticky, you may add the message to your gadgets.
Best Examples of High-Fidelity Wireframes:
Digital, Code-free Prototypes
No matter what digital product or experience you’re making, you’ll need to make a digital prototype. This is where digital prototyping tools come into play. It enables designers to produce functional prototypes that are visually appealing and functionally similar to the final user interface.
Designers may illustrate how their experience will appear and feel, giving product teams vital input before they launch their final product. Unfortunately, they require a lot of time and energy to produce. Therefore many product teams choose faster and simpler alternatives like paper prototyping sooner in the design process.
Coded Prototypes
Regarding appearance and functionality, coded prototypes are the nearest to the final product designers will create. This prototype makes them ideal for getting last-minute input from customers before releasing a product. Yet, not everyone can create code prototypes. However, many designers lack the requisite coding skills and need assistance to produce such advanced prototypes.
When Should You Use High-Fidelity Wireframes?
When designers have finished mockups and produced at least one user flow for testing, UX teams should only go on to high-fidelity prototyping after they have completed low-fidelity prototyping. For the initial round of usability research, these mockups need clickable links and components, color, and text, but not interactions, animations, or transitions. It is helpful to have a high-fidelity prototype to test page transitions and how items behave on the page. UX designers may also test user experience through interactions, animations, and changes. So the last step in the design process should be the creation of a high-fidelity prototype before passing the project over to engineering.
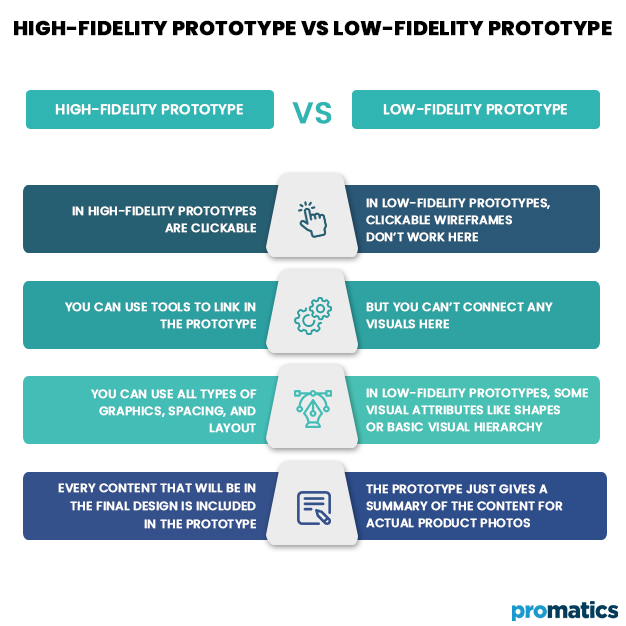
Low-Fidelity vs. High-Fidelity: Comparison Table
Let’s look over the differences between high-fidelity and low-fidelity prototypes.
Conclusion
Can you use both in your project? Yes, you can. As we told you before, you must use a hi-fi prototype at the end of your design process. But before that, you must test your design in low-fi. At the same time, a low-fidelity prototype is sufficient if you don’t need to evaluate the product’s look or functioning. However, designers almost always need high-fidelity prototyping to determine how users interact with prototypes. We propose hi-fi prototyping if you want to create a user-friendly app. It may save you time and money on UI and more. I hope you have a complete idea of the differences between low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes.
Still have your concerns?
Your concerns are legit, and we know how to deal with them. Hook us up for a discussion, no strings attached, and we will show how we can add value to your operations!