Cloud-Based vs Edge-Based IoT Software Development: Which Is Better?
As enterprises across the US and global markets accelerate digital transformation, the Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a critical enabler of intelligent operations. Today, every forward-thinking IoT software development company is helping organizations across manufacturing plants, logistics networks, energy systems, and smart infrastructure leverage connected devices and sensors that continuously generate massive volumes of real-time data.
As IoT ecosystems expand at scale, enterprises face a fundamental architectural question that shapes long-term success:
Should IoT data be processed at the Edge or in the Cloud?
For any IoT software development company, this decision directly impacts system responsiveness, scalability, security, operational costs, and overall return on investment. While both cloud-based and edge-based IoT software development models enable data-driven intelligence, they differ significantly in how and where data is processed.
Rather than being a simple either-or choice, the comparison between Edge and Cloud computing requires a deeper understanding of enterprise IoT workloads, data criticality, latency requirements, and business objectives. Modern IoT software development companies increasingly recognize that different use cases demand different processing strategies.
This blog explores the strengths, limitations, and ideal use cases of both Edge and Cloud approaches and explains why hybrid architectures are rapidly becoming the standard for modern IoT systems developed by leading IoT software development companies worldwide.
The Role of Data in Enterprise IoT Ecosystems
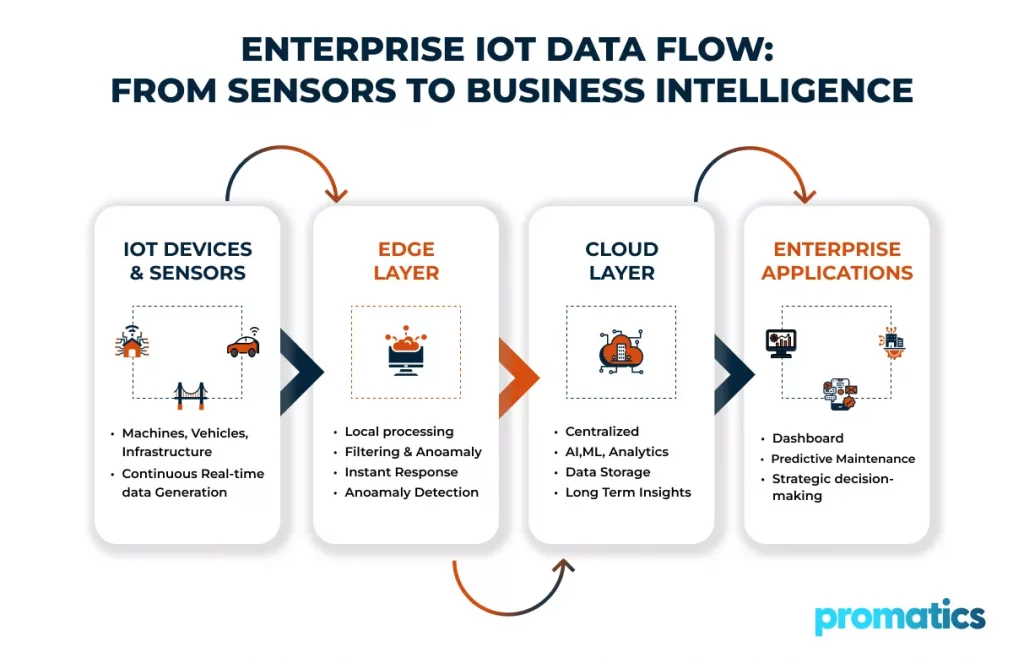
Data is the foundation of every IoT system. Sensors embedded in machines, vehicles, infrastructure, and industrial equipment continuously capture metrics such as temperature, vibration, pressure, energy usage, location, and performance indicators. When processed effectively, this data enables enterprises to optimize operations, improve safety, predict failures, and automate decision-making.
However, IoT data presents unique challenges:
- It is continuous and high-volume
- It is generated across distributed environments
- Many use cases are time-sensitive
A single industrial facility can generate terabytes of sensor data daily. Sending all raw data to centralized cloud systems can introduce latency, increase bandwidth costs, and create dependency on network availability. At the same time, cloud platforms remain essential for aggregating data across locations and generating long-term insights.
The real challenge in IoT software development is not deciding where data should live, but where it should be processed to balance speed, reliability, and intelligence.
What Is Edge Computing in IoT Software Development?
Edge computing refers to processing data close to its source on IoT devices, gateways, or local servers rather than transmitting everything to remote cloud infrastructure. By reducing the distance data must travel, edge computing minimizes latency and enables near-instant responses.
In enterprise IoT environments, edge systems are deployed within factories, warehouses, vehicles, power plants, and remote facilities. These systems handle real-time workloads such as equipment monitoring, anomaly detection, process control, and automated responses.
For example, in a manufacturing environment, edge analytics can instantly detect abnormal machine behavior and trigger corrective actions within milliseconds. This level of responsiveness is critical for preventing equipment damage, ensuring safety, and minimizing downtime.
Edge-based IoT software development is particularly valuable when applications must operate reliably even with limited or intermittent network connectivity.
Advantages of Edge-Based IoT Software Development
Edge computing offers several key benefits for enterprise IoT use cases:
- Ultra-Low Latency
Edge processing enables real-time decision-making, making it ideal for industrial automation, robotics, predictive maintenance, and safety-critical systems.
- Reduced Bandwidth Usage
By processing data locally, only relevant insights or summaries are sent to the cloud, significantly reducing data transmission and storage costs.
- Improved Operational Reliability
Edge systems can continue operating even during network outages, ensuring continuity for mission-critical processes.
- Enhanced Data Privacy and Security
Sensitive data can be processed locally, reducing exposure to external networks and supporting compliance requirements.
By enabling intelligent action at the source, edge computing transforms IoT devices from passive data collectors into autonomous, responsive systems.
What Is Cloud Computing in IoT Development?
Cloud computing in IoT involves storing, managing, and analyzing data in centralized data centers operated by IoT software development companies. These platforms offer virtually unlimited computational power, high availability, and global accessibility.
In enterprise IoT software development, the cloud acts as the central intelligence layer. It aggregates data from multiple edge locations to support advanced analytics, machine learning, predictive modeling, and system-wide orchestration.
For instance, while an edge device may analyze sensor data for a single machine, cloud platforms can analyze historical data across multiple facilities and regions to identify patterns, forecast demand, and optimize operations at scale.
Cloud-based IoT development is essential for organizations that require centralized visibility, long-term insights, and scalable data processing.
Advantages of Cloud-Based IoT Development
Cloud platforms provide several strategic benefits for enterprise IoT initiatives:
- Massive Scalability
Cloud infrastructure can support millions of connected devices across multiple geographies without performance degradation.
- Advanced Analytics and AI Capabilities
Cloud environments enable predictive analytics, machine learning, and AI-driven optimization using large historical datasets.
- Cost-Efficient Infrastructure
Pay-as-you-go pricing models reduce upfront capital investment and allow enterprises to scale resources as needed.
- Seamless Integration
Cloud APIs make it easy to integrate IoT data with enterprise applications, analytics dashboards, and business intelligence tools.
Cloud computing delivers the macro-level intelligence required for strategic planning and long-term optimization.
Edge vs Cloud: Key Differences in IoT Software Development
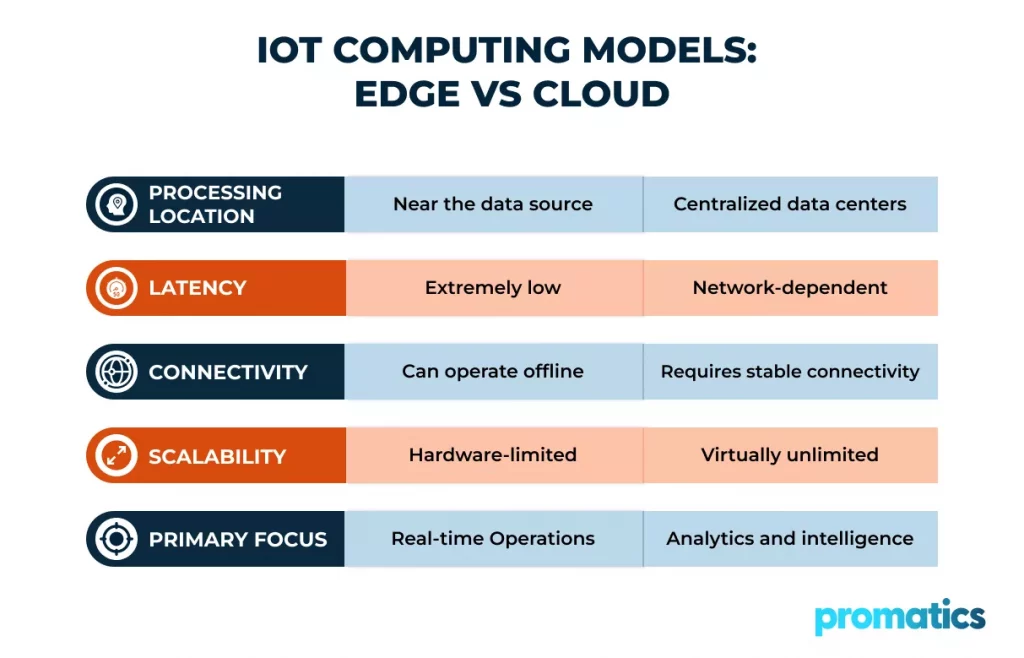
Edge computing prioritises speed and operational independence while cloud computing systems design for increased capacity and analytical capabilities. The majority of enterprise IoT systems need both technologies to achieve proper system operation.
Why Speed Matters in Enterprise IoT Systems
In industries such as manufacturing, energy, logistics, and transportation, milliseconds can impact safety, efficiency, and profitability. Delayed responses to equipment anomalies or environmental changes can result in downtime, financial loss, or safety risks.
Edge computing addresses these challenges by enabling immediate, localized responses. However, not all IoT workloads require instant action. Strategic functions such as predictive maintenance planning, asset optimization, and demand forecasting depend on large-scale data analysis, which cloud platforms handle more effectively.
Understanding which decisions require real-time processing and which can tolerate latency is critical to designing a successful IoT architecture.ng landscape.
Real-World Enterprise IoT Use Cases
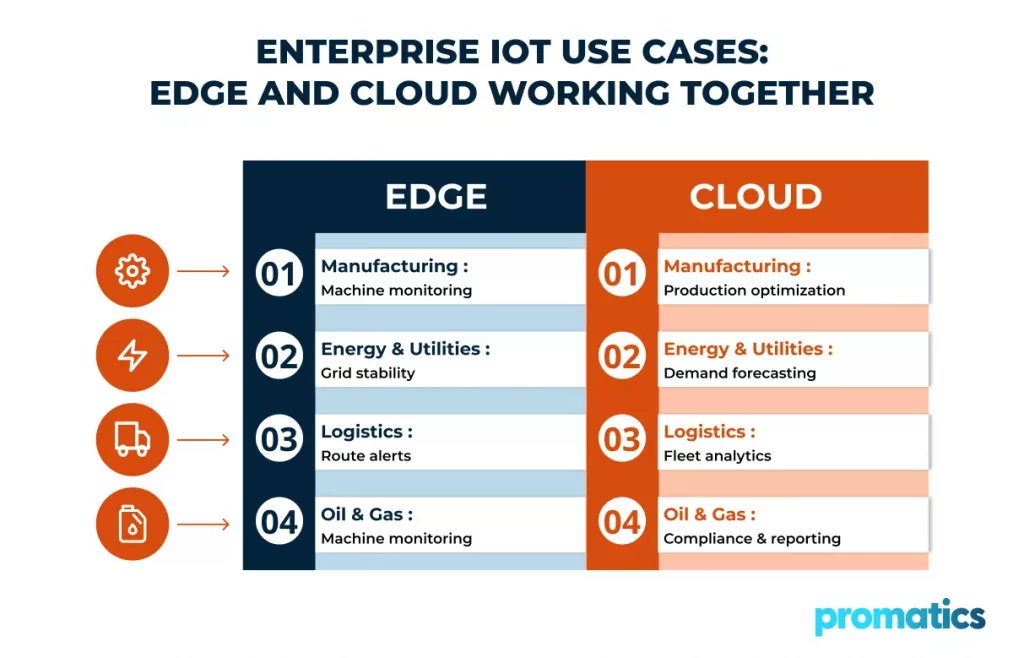
- Manufacturing and Industrial Automation
Edge systems monitor machines and robotic processes in real time, while cloud platforms analyze production trends across facilities to improve efficiency and quality.
- Smart Energy and Utilities
Edge devices manage local grid stability and detect anomalies, while cloud analytics forecast demand and optimize energy distribution across regions.
- Logistics and Fleet Management
Edge computing supports real-time route optimization and safety alerts, while cloud platforms provide fleet-wide insights and predictive maintenance data.
- Oil and Gas Operations
Edge analytics detect pressure changes or leaks instantly at remote sites, while cloud systems analyze historical data for compliance and operational optimization.
These use cases highlight how edge and cloud technologies complement each other within enterprise IoT ecosystems.
The Rise of Hybrid Edge–Cloud IoT Architectures
Rather than choosing between edge or cloud, enterprises increasingly adopt hybrid IoT architectures. In this approach:
Edge systems handle time-critical processing and automation
Cloud platforms aggregate data and deliver advanced analytics
Insights flow continuously between edge and cloud layers
This architecture enables real-time responsiveness while maintaining centralized intelligence and scalability. Hybrid models also future-proof IoT systems, allowing enterprises to adapt as data volumes and operational requirements grow.
AI and Machine Learning in IoT Systems
Artificial intelligence plays a growing role in IoT by transforming raw sensor data into actionable intelligence. In enterprise deployments:
- AI models are trained in the cloud using large historical datasets
- Optimized models are deployed at the edge for real-time inference
This continuous learning cycle enables adaptive IoT systems that improve performance over time while maintaining instant responsiveness at the device level.
Cost and ROI Considerations
Cloud-based IoT solutions offer flexibility and scalability but can increase operational costs when large volumes of data are transmitted continuously. Edge-based IoT software development may require initial hardware investment, but it reduces bandwidth usage and minimizes latency-related downtime.
Many enterprises find that hybrid architectures deliver the strongest ROI, balancing real-time efficiency with centralized analytics and long-term insight.
How to Choose the Right IoT Development Approach
Selecting the right IoT architecture depends on several factors:
- Latency and real-time requirements
- Data sensitivity and regulatory compliance
- Network reliability
- Scalability and future growth
- Existing infrastructure
An experienced IoT software development company can help evaluate these factors and design a solution aligned with enterprise objectives and global deployment needs.
Conclusion
In enterprise IoT software development, both edge and cloud computing play essential roles. Edge computing enables real-time responsiveness at the source, while cloud computing delivers centralized intelligence and long-term insights. When combined thoughtfully, these technologies allow organizations to act instantly while continuously learning from data at scale.
As IoT ecosystems expand across industries and global markets, hybrid edge–cloud architectures are becoming the foundation of connected intelligence, helping enterprises balance speed, scalability, security, and operational resilience.
Designing a secure, scalable, and high-performing IoT ecosystem requires more than selecting the right technologies it demands clear architectural strategy and execution expertise. Promatics Technologies helps enterprises design and implement IoT solutions that seamlessly integrate edge and cloud environments, enabling real-time intelligence and measurable business outcomes.Looking to build or modernize your IoT ecosystem? Connect with our experts to explore how a future-ready IoT architecture can drive efficiency, reliability, and long-term value for your business.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does an IoT software development company do?
An IoT software development company builds end-to-end IoT solutions, including device integration, data processing, edge and cloud architecture, security, analytics, and scalable enterprise applications.
2. How do IoT development services support enterprise operations?
IoT development services enable real-time monitoring, automation, predictive insights, and centralized management, helping enterprises improve efficiency and reduce operational risks.
3. When should businesses choose edge-based IoT software development?
Edge-based IoT software development is ideal for latency-sensitive applications that require immediate responses, such as industrial automation, safety systems, and equipment monitoring.
4. Why is a hybrid edge cloud approach recommended?
Hybrid architectures combine the speed of edge computing with the scalability and intelligence of cloud platforms, making them suitable for enterprise IoT deployments across multiple locations.
5. How do I choose the right IoT app development company?
Enterprises should evaluate technical expertise, experience with edge and cloud systems, security practices, scalability capabilities, and industry-specific knowledge.
