Native vs. Hybrid App Development Cost Comparison: A Practical Guide for Modern Businesses

Mobile applications have evolved far beyond supporting digital tools. Today, they function as core business platforms that drive customer engagement, operational efficiency, and scalable growth. From eCommerce and digital payments to healthcare, logistics, and enterprise systems, mobile apps now sit at the center of modern business strategy.
As user expectations continue to rise, businesses are increasingly evaluating hybrid vs native apps to deliver fast, secure, and high-performing experiences across devices. This makes the choice between hybrid mobile application development and native development more than a technical decision; it directly impacts development cost, time-to-market, scalability, and long-term maintenance.
This blog explores the cost, performance, and long-term ownership trade-offs between native and cross-platform mobile app development approaches. It also examines how modern hybrid app frameworks, single codebase app development, and AI-driven backends are shaping architecture decisions for startups and enterprises alike. Read on to understand which approach aligns best with your business goals and long-term growth plans.
Understanding Mobile App Development Approaches
Before comparing costs, it is important to understand how native and hybrid app development differ at an architectural level.
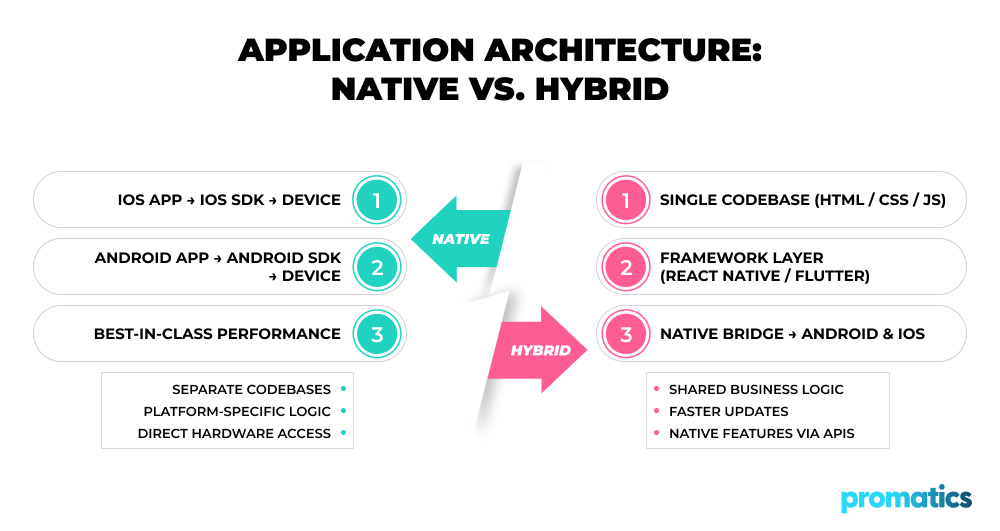
Native App Development
Native app development involves building applications specifically for a single platform most commonly Android or iOS using platform-specific programming languages, SDKs, and tools.
- iOS apps are developed using Swift or Objective-C with Apple’s Xcode
- Android apps are built using Kotlin or Java with Android Studio
Because native apps are compiled directly for the operating system, they have unrestricted access to device hardware and system APIs.
Advantages of Native App Development
Native apps are often chosen for their technical strengths, including:
- High-performance execution and responsiveness
- Smooth animations and platform-consistent UI/UX
- Full access to device features such as camera, GPS, sensors, biometrics, and Bluetooth
- Strong offline capabilities
These advantages make native development well-suited for performance-intensive and hardware-dependent applications.
Cost Implications of Native Architecture
While native apps deliver excellent performance, they come with higher development and maintenance costs. Native development typically requires:
- Separate codebases for Android and iOS
- Platform-specific development expertise
- Independent testing, QA, and release cycles
- Ongoing dual maintenance and updates
Over time, these factors increase both upfront investment and long-term total cost of ownership.
Hybrid App Development
Hybrid app development uses a single shared codebase that runs across multiple platforms. These applications are built using web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript and are wrapped within a native container.
Popular hybrid app frameworks include:
- React Native
- Flutter
- Ionic
Hybrid apps rely on web and native app integration, allowing developers to reuse business logic while still accessing native device features through APIs and plugins.
Advantages of Hybrid App Development
Hybrid app development has gained strong adoption due to its efficiency and scalability:
- Faster development and deployment
- Lower upfront investment
- A unified codebase for Android and iOS
- Simplified maintenance and updates
This approach has fueled demand for hybrid mobile application development, particularly among startups, enterprises, and businesses seeking faster time-to-market without sacrificing future scalability.
Key Factors That Influence Mobile App Development Cost
Regardless of whether an app is native or hybrid, several core factors shape development cost.
- Application Complexity and Feature Scope
Applications with basic functionality, such as authentication, content display, and dashboards, cost significantly less than apps that require:
- Real-time data synchronization
- Payment processing
- AI-powered personalization
- Advanced analytics and automation
Hybrid architectures often reduce duplication for complex features, helping control overall cost.
- UI/UX and Platform-Specific Design
Native apps typically require platform-specific UI adjustments to align with Android and iOS design guidelines. This increases both design and development effort.
Hybrid app design and development allows shared UI components across platforms, reducing cost while maintaining visual consistency.
- Backend Infrastructure and Integrations
Backend development represents a significant portion of total app cost and generally remains consistent across native and hybrid apps. This includes:
- API development
- Cloud infrastructure
- Third-party integrations
- AI services and data pipelines
- Testing, QA, and Deployment
Native apps require separate testing cycles for Android and iOS. Hybrid apps simplify QA through shared logic but still require platform validation to ensure consistent behavior.
- Maintenance and Update Cycles
Long-term costs include:
- Bug fixes
- OS compatibility updates
- Security patches
- Feature enhancements
Hybrid app maintenance is typically more cost-efficient due to a unified codebase.
Initial Development Cost: Native vs. Hybrid

Native App Cost Structure
Native development involves building and maintaining two separate applications.
Key cost drivers include:
- Separate development teams or specialized skills
- Parallel development timelines
- Independent design and testing efforts
Advanced features such as AR, real-time processing, or on-device AI further increase development cost.
Hybrid App Cost Structure
Hybrid development significantly reduces duplication by leveraging single codebase app development.
Hybrid apps generally cost less initially because they involve:
- One development team
- Faster development cycles
- Shared UI and business logic
This directly lowers the hybrid app development cost, particularly for multi-platform launches.
High-Level Cost Comparison
| Factor | Native Apps | Hybrid Apps |
| Codebase | Separate | Single |
| Initial Cost | High | Moderate |
| Time-to-Market | Slower | Faster |
| Maintenance | Higher | Lower |
Long-Term Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Initial development cost is only part of the financial picture.
Native App Maintenance
Native apps require:
- Dual maintenance cycles
- Platform-specific bug fixes
- Increased testing after OS updates
- Higher cumulative costs over time
Hybrid App Maintenance
Hybrid apps benefit from:
- Unified maintenance and updates
- Faster rollout across platforms
- Lower long-term engineering overhead
For many organizations, hybrid apps offer a more predictable and manageable TCO.
Performance, UX, and Practical Trade-Offs
Native Performance Benefits
- Superior responsiveness
- Optimized graphics rendering
- Reliable offline capabilities
Modern Hybrid App Performance
Advancements in hybrid mobile app technology have significantly narrowed the performance gap.
For most business, enterprise, and AI-enabled apps:
- Performance is more than sufficient
- User experience is comparable to native
- Backend-driven logic minimizes frontend strain
Choosing native purely for perceived performance can often lead to unnecessary overspending.
Security Considerations in Hybrid and Native Apps
Hybrid app security is often misunderstood.
In practice, security depends more on architecture than on platform choice. Critical factors include:
- Backend security design
- API protection
- Authentication and authorization
- Data encryption and regulatory compliance
When implemented correctly, hybrid app security is comparable to native apps and suitable for enterprise use.
The Role of AI in Native vs. Hybrid App Development
AI has become a defining capability in modern mobile applications.
Common AI Use Cases
- Chatbots and conversational interfaces
- Recommendation engines
- Image, voice, and text processing
- Predictive analytics and automation
AI Cost Drivers
AI costs are primarily backend-focused and include:
- Model hosting
- Inference processing
- API usage
- Data storage and compliance
These costs are largely independent of frontend architecture.
AI in Native Apps
Native apps enable:
- On-device AI processing
- Offline intelligence
- Low-latency performance
However, this significantly increases development complexity and cost.
AI in Hybrid Apps
Hybrid apps typically integrate AI through cloud APIs, offering:
- Faster AI implementation
- Lower frontend cost impact
- Easier scalability
For most business applications, hybrid + AI provides the best balance of cost and capability.
When Native Makes Sense for AI
Native development is justified primarily when:
- AI must operate offline
- Real-time sensor processing is required
- Hardware-level optimization is critical
In most other scenarios, hybrid architectures are sufficient.
When Hybrid Is Sufficient
For most business applications, AI is integrated via cloud APIs. In these cases, hybrid apps provide faster implementation, easier scalability, and lower frontend cost impact.
Use-Case-Based Cost Effectiveness
Native plus AI is suitable for AR/VR applications, fitness tracking with sensors, and offline-first intelligence. Hybrid plus AI works well for enterprise applications, dashboards, chatbots, recommendation systems, and MVPs.
When Native + AI Makes Sense
- AR/VR applications
- Health and fitness tracking with sensors
- Offline-first intelligence
When Hybrid + AI Is the Better Choice
- Enterprise applications
- AI-powered dashboards
- Chatbots and recommendation systems
- Hybrid app development for startups and MVPs
Hidden and Indirect Costs to Consider
Many businesses overlook indirect costs such as:
- AI API scaling expenses
- Performance optimization
- Data privacy and regulatory compliance
- Future migration or re-architecture
Ignoring these factors can significantly inflate long-term expenses.
Why Businesses Choose Promatics Technologies for Hybrid App Development
Choosing the right architecture is only part of the equation. Execution quality determines long-term success.
Promatics Technologies supports startups, enterprises, and global organizations in designing and building scalable hybrid mobile applications.
With expertise in React Native and Flutter, Promatics delivers hybrid solutions focused on performance, maintainability, and long-term scalability. A business-first engineering approach ensures solutions align with ROI goals, budgets, and growth plans.
Promatics provides end-to-end services, including product discovery, UI/UX design, hybrid app development for Android and iOS, backend and AI integration, testing, deployment, and ongoing maintenance.
Choosing the Right App Strategy and the Right Partner
The native vs. hybrid app development debate is no longer about which approach is universally better. It is about selecting the most practical, scalable, and cost-effective solution for your specific business context.
Native apps offer maximum performance and control but at a higher cost. Hybrid apps, powered by modern frameworks and cloud-based AI, deliver faster time-to-market, lower total cost of ownership, and performance that meets the needs of most modern applications.
AI does not automatically require native development. In most cases, hybrid frontends paired with intelligent backend systems deliver exceptional results without unnecessary expense.
If you are evaluating hybrid vs native apps, planning a new mobile product, or looking to optimize the cost of hybrid mobile app development without compromising quality, Promatics Technologies can help.
Ready to Build the Right Mobile App? Connect with Promatics Technologies today to build a secure, scalable, and future-ready mobile application aligned with your business goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which is more cost-effective: native or hybrid app development?
Hybrid app development is generally more cost-effective due to shared codebases and faster development.
Are hybrid apps suitable for enterprise use?
Yes. Enterprise hybrid app development is widely adopted for internal tools and scalable platforms.
Can hybrid apps run on both Android and iOS?
Yes. Hybrid app development supports Android and iOS using a single codebase.
Which hybrid app framework is best?
React Native and Flutter are among the most widely used hybrid app development frameworks today.
Is hybrid app development secure?
Yes. Hybrid app security depends on architecture and implementation quality, not the framework alone.
