How Much Does it Cost to Build a SaaS Platform in 2025?

SaaS (Software as a Service) has come out to become one of the most popular business models in the software market. Businesses are now switching to SaaS as the demand for flexible, scalable, and user-friendly software grows to drive revenue, improve productivity, and enhance customer experience. However, the SaaS product is anything but easy to build, requiring considerable amounts of time, investment, and a good deal of forethought into the approach to be taken. In this article, we will study the various factors affecting the SaaS development costs, methods to estimate the cost efficiently, and sneaky expenses that can pop up during and after the development. Whether you are considering launching a new SaaS product from the ground up or are still somewhere in the early stages of a development process, understanding these key cost factors will arm you with greater confidence to navigate through the SaaS world ahead.
Factors Influencing SaaS Development Costs
A. Product Complexity
The complexity of the SaaS product plays a significant role in determining the development costs. The more features and functionalities a SaaS product has, the higher the costs will be. Here’s a breakdown of the aspects of complexity that influence development costs:
- Core Features: Basic SaaS products may have features like user registration, dashboards, or basic reporting capabilities. Yet with increasing scale and complexity of the features-increased automation workflows, advanced analytics, and multi-level security to name a few developed costs.
- Customised and Personalised: SaaS products increase their value: Customised client-specific features greatly increase development time and effort; for example, custom dashboards, user roles, and permissions would require highly specialised coding, which adds another significant cost to the deal.
- Real-time Capabilities: Most modern enterprise software applications use real-time interactions chats, data syncing, or notifications. The implementation of these features calls for a very robust back-end development and infrastructure, thus raising the cost.
- Security: This is non-negotiable for SaaS development, given that sensitive customer data is at stake. Costs will increase with the implementation of high-level security measures, from data encryption and secure user authentication to compliance with regulations (GDPR, HIPAA).
B. Technology Stack
The technology stack describes the various tools, programming languages, and frameworks that are used to build SaaS applications; this is something that has a good impact on how an application is developed and on its long-term capacity to grow. A deeper analysis of how technology directly impacts SaaS development costs is given here:
- Frontend and Backend Tech Stack: A modern SaaS requires the proper selection of the frontend (React, Angular) and backend (Node.js, Django). Sophisticated frameworks and libraries usually demand capable developers, which increases labor costs. Time and resources devoted to training developers in a specific technology are added on top of whatever initial cost it takes.
- Cloud Services: SaaS applications are vulnerable to much of the service because of the substantial dependency on cloud services (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud), which scale and provide service reliability.
- The charges may be levied per usage depending on data storage, compute power, and traffic volume, making cloud hosting a long-term cost recognition rather than one-time.
- Database Management: The database is the heart and soul of any SaaS application. The cost of setting, maintaining, and scaling up is dictated by whether one goes with a relational database like MySQL or a non-relational database like MongoDB. Distributed databases or real-time data processing tends to be more expensive for development since they require more expertise.
C. Team Composition and Expertise
A highly skilled development team is essential for creating a quality SaaS product. The size and experience level of the team significantly influences the development costs. Here’s how:
- Team Size: Larger teams inflate the cost. In-house teams typically comprise developers, designers, testers, project managers, and some other specialists. More teams mean added overhead costs on the project with salaries, training, and communication as possible examples.
- Experience Level: Higher will be the ask from the senior front developers who specialise in these technologies. You may go for graduate and senior developer combinations to have the balance between better expertise and comparatively lower wages, while careful management will also be needed to retain quality.
- In-House vs. Outsourced Development: Choosing to outsource to a third party some aspects of development should save money in overall development. But this has communication problems and maybe more unusually slow. On the other hand, hiring development at your firm will give you full command and control over the project at a higher cost from the likes of office space, benefits, and recruitment.
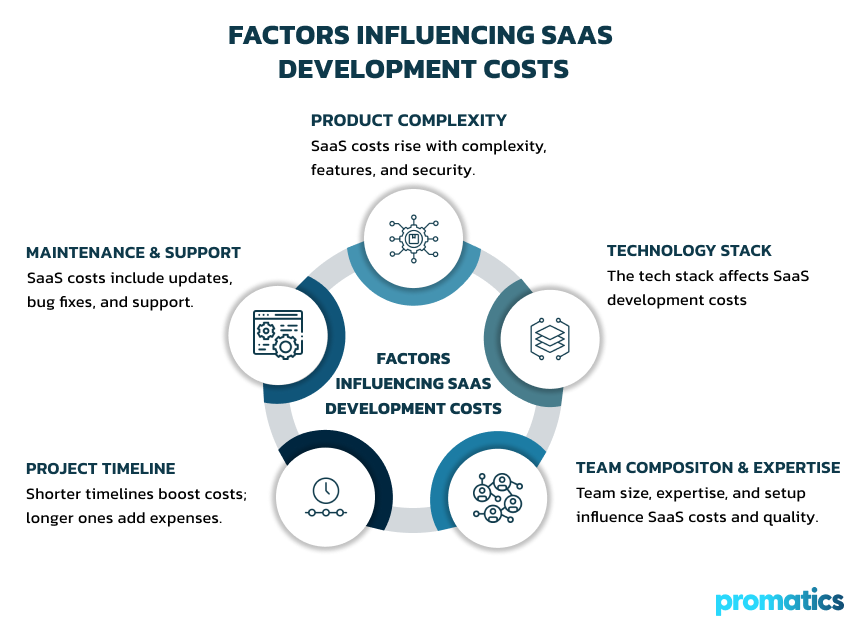
D. Project Timeline
The timeline you set for development directly impacts the cost of the project. To shorten the development timeline, more developers would be working long into the night, which increases the cost of labor. However, with a longer timeline, a team may not have to put in overtime, thereby causing less addition to the cost of the project but increasing the overall time as well.
- Short Timeline: When a release requires a few months, developers might have to work overtime, resulting in inflated labor costs or additional resources.
- Extended Timeline: A longer timeline may mean reduced immediate costs, but such ongoing expenses as server costs, and maintenance costs will continue to accrue.
E. Maintenance and Support
SaaS development doesn’t end with the launch of the product. Maintenance and support are crucial aspects that add to the total cost over the product’s lifecycle.
- Ongoing Updates: SaaS platforms require regular updates to fix bugs, improve functionality, and add new features. These updates may require additional development work, leading to increased costs.
- Bug Fixes: Even after the product is launched, issues may arise that need immediate resolution, particularly in the early stages. This requires dedicated developers and QA professionals to manage, potentially increasing support costs.
- Customer Support: As your SaaS product gains users, you will need to provide customer support. This may include hiring dedicated support staff, creating knowledge bases, and using software like ticketing systems or live chat services, which can add significant ongoing costs.
Cost Estimation for SaaS Development
Cost estimation for SaaS development is crucial to understanding the overall financial commitment for the entire project. SaaS development costs can vary greatly depending on several factors such as complexity, features, and team composition. Here’s a detailed look into how costs break down:
A. SaaS Product Phases and Their Associated Costs
1. Discovery Phase:
This phase typically involves the analysis of your target audience, competitors, and business objectives, and the creation of initial designs. The average cost for this phase is usually between $10,000 to $30,000. Costs here are associated with market research, business analysis, and developing wireframes or prototypes. The complexity of the product can influence these costs, particularly if the initial concept needs to be refined multiple times.
2. Development Phase:
Most manufacturing for SaaS takes place here, where the product’s core functionality, backend, frontend, and integrations with other systems are created. The development phase is highly dependent on the complexity of the project and the expertise of the development team. To summarize, developing a basic SaaS app might cost between $50,000 to $200,000, whereas for more advanced or enterprise-level ones, it is possible to exceed $500,000.
The costs will depend on:
- Frontend Development: The essence of Frontend Services varies between $30K to $70K depending on the design complexity and the amount of user interface elements that need to be created.
- Backend Development: The costs may range from $50K to $150K for the backend services and database management again depending on the project scope data handling requirement and the server architecture.
- Integrations and APIs: Integration of third-party services such as payment gateways, CRM systems, and marketing tools typically add $5K to $50K based on the complexity of the integrations.
3. Testing and QA Phase:
Once the application is developed, it will begin with various tests, such as functional, security, performance, and usability testing. Especially ensuring a good user experience. The cost for the testing and QA phase typically ranges from $10,000 to $50,000. In some cases, the incorporation of automated testing frameworks will further add costs because you will need other tools and resources to do that.
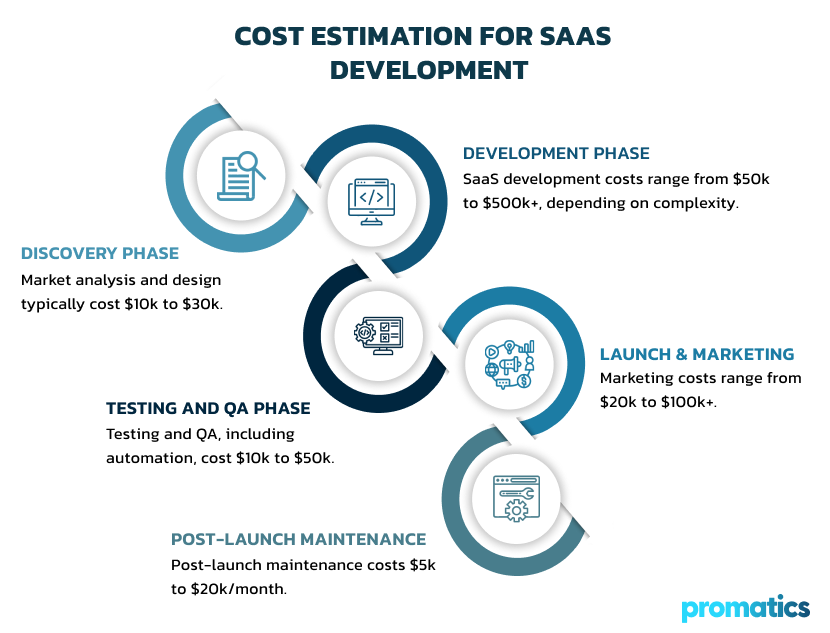
4. Launch and Marketing Costs:
Apart from launching the product, there are marketing endeavors such as search engine optimization, advertisements, content marketing, influencer marketing, etc. The marketing is more or less going to kick off from anything between the ballpark figure of $20,000 to $100,000 or even more, depending on your target audience, channels of advertisement, and the end goal of the campaign.
5. Post-launch Maintenance and Support:
Post-launch costs include ongoing updates, security patches, scaling the infrastructure, and providing customer support. A basic maintenance plan can cost between $5,000 to $20,000 per month depending on the frequency of updates and the complexity of the platform.
Pricing Models for SaaS Development
When it comes to pricing SaaS development, there are several pricing models that developers and agencies often use. Here’s a breakdown:
1. Hourly Rate Model
- Typical Rate: Development agencies or freelance developers will usually average between $50 and $150/hour for SaaS development depending on the expertise and location of the development team.
- The pricing model here is one mostly employed in making smaller projects or work where the scope does not have a clear shape or will most probably evolve. When features become more complex, the total cost will also grow, as the number of hours required will go up.
2. Fixed Price Model
- Typical Cost: A fixed-price contract involves setting a predetermined budget for the entire development process, often between $40,000 to $500,000, based on project complexity.
- This model is ideal when the project’s requirements and features are clearly defined from the outset. It provides a clear understanding of the total costs upfront but might require flexibility for any unforeseen changes in scope.
3. Subscription Model (Ongoing Service)
- Some SaaS developers offer an ongoing subscription model where you pay a fixed amount each month or year for ongoing development, maintenance, and support. Costs for this can range between $10,000 to $50,000 per month depending on the complexity and requirements of the SaaS platform.
4. Dedicated Team Model
- Cost: For larger SaaS projects, you might opt for a dedicated team. This model typically includes a full development team working exclusively on your project for an agreed period. The cost is usually around $50,000 to $150,000 per month for a dedicated team, depending on the size and expertise of the team.
5. Cloud Hosting and Infrastructure Costs
Cloud services are integral to SaaS products, but they also come with their own cost structure. Here’s a breakdown of typical cloud service costs:
- AWS (Amazon Web Services): Prices typically start at $100 to $500 per month for small-scale products, but can scale up to $2,000 to $10,000+ per month for more complex, data-heavy SaaS platforms.
- Azure/Google Cloud: These platforms typically offer competitive pricing. A small SaaS app may incur $100 to $1,000 per month, while larger-scale applications can expect monthly costs ranging from $3,000 to $15,000 depending on usage and scale.
Hidden Expenses in SaaS Development
Apart from the standard development and maintenance costs, there are several hidden expenses that can significantly increase the overall cost of SaaS development.
A. Unexpected Scaling Costs:
As your SaaS product grows in popularity, so do the costs associated with scaling your infrastructure. These include:
- Server Infrastructure: The service provider must add these to the server infrastructure every time a new user comes online (cloud services, databases, and storage). The cost of doing this can range anywhere from $1,000 per month to over $10,000, depending on usage.
- Data Storage: A SaaS having huge data of the user will require a large data storage base. At an average, cloud data storage can range from $100 to $1,000 per month.
B. Customer Support:
After launching your product, you’ll now need to devote money in customer support, which includes hiring dedicated staff, maintaining live chat systems, and setting up automated response systems. Customer support has the cost of $2,000 and can go up to $10,000 per month on a pure variable basis, depending on the number of users and the level of support provided.
C. Security and Compliance:
To comply with regulations such as GDPR, PCI-DSS, and HIPAA, the SaaS platforms need to deploy advanced security features. In encryption, using penetration testing and performing annual security audits can range anywhere between $5,000 and $20,000 per year, depending on the type of business and the nature of customer data.
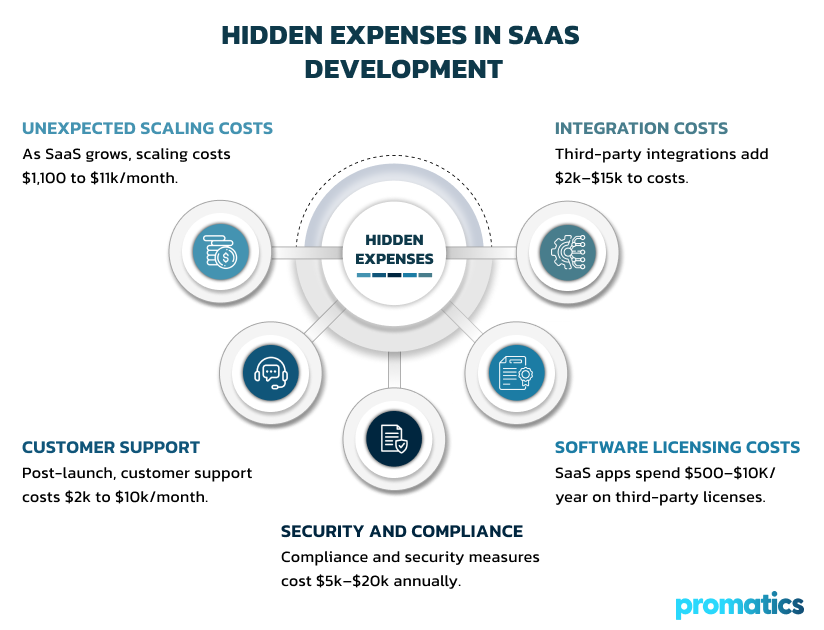
D. Software Licensing Costs:
Many SaaS applications must pay an additional fee for using third-party tools or software libraries. The cost to acquire these licenses may range from $500 to $10,000 a year on account of their popularity.
E. Integration Costs:
Integration with commonly used third-party services to fulfill payment gateways, marketing tools, and/or CRM systems will also add extra costs. Depending on how complex the services are and how complex the integration is, integrating could raise the total development price tag by $2,000-$15,000.
Conclusion: Managing and Navigating SaaS Development Costs
Grasping different aspects, the pricing model and hidden costs in SaaS helps in better budget management. Realistic cost estimates made based on the complexity and the scale of your SaaS project and an intelligent and realistic view of ongoing operational costs can help you plan better.
Every phase in the lifecycle of SaaS development discovery through maintenance and post-launch support has cost issues unique to that phase. Using cost-effective means of development, such as making maximum use of available open-source tools, adopting agile methodology, and outsourcing when possible, can help you very well manage your SaaS development budget while delivering a quality solution.
Along with this, realizing what the ongoing costs through cloud hosting, support, and growth will look like will help maintain sustainability and effectively keep profits going for many years for your SaaS platform. Future trends in SaaS, such as the rise of AI integration and no-code platforms, could influence both the cost of development and how efficient the delivery process becomes.
Taking all these revelations and pointers together can really help you avoid the many pitfalls while meeting the needs of your users and business objectives with a well-crafted product.

