May Decoding the Mobile App Backend: The Engine Under the Hood

Mobile apps have become essential tools for companies and consumers in the fast-changing digital environment. Although the user interface—the front end of an app—is what people engage with, the backend drives the app’s features, guarantees smooth operation, data management, and security. This all encompassing book investigates mobile app backend development‘s complexity by looking at its parts, kinds, tools, and best practices.
Grasping Mobile App Backend
The backend of a mobile app is the server-side infrastructure controlling the application’s logic, database interactions, authentication, and general functionality. Processing user requests, executing tasks, and providing replies, it supports the frontend. Even the most aesthetically pleasing application would lack functionality and reactivity without a strong backend.
The mobile app backend’s main duties are:
- Data Management: Efficiently storing, retrieving, and updating data.
- Ensuring safe access: to the app’s features and data.
- Business logic implementation: Executing the fundamental functions and rules of the application.
- Integrating with third-party services: Interfacing with outside APIs and services to improve app functionality.
A well-organised backend guarantees scalability, security, and maintainability—qualities absolutely vital for the long-term success of the application.
Basic Elements of Mobile App Backend
1. Server
Processing frontend requests and running business logic, the server serves as the central hub. A server can be:
- Cloud-Based: Platforms such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure provide reasonably priced and scalable options.
- Dedicated: Perfect for uses calling for great security and performance, such as banking apps.
Scalability needs, budgetary limits, and particular application requirements all influence the decision between cloud-based and dedicated servers.
2. Database
Databases handle and keep the application data. There are two main kinds of them:
- SQL (Structured Query Language): Appropriate for structured data with specified relationships. MySQL and PostgreSQL are two instances.
- NoSQL: Perfect for unstructured data, NoSQL provides scalability and flexibility. Among them are Firebase and MongoDB.
Efficient data management and retrieval depend on the choice of a suitable database type, which directly affects the performance of the application.
3. Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
APIs help the backend and frontend interact. They let the program effortlessly send and receive data. Common API designs are:
- REST (Representational State Transfer): Popular because of its simplicity and scalability.
- GraphQL: Reduces the data sent by letting users ask for particular information.
Good API design guarantees quick data transfer, improves application performance, and streamlines third-party service integration.
4. Authorisation and Authentication
It is absolutely vital to make sure users are who they say they are. While authorisation decides what user resources he or she may access, authentication confirms user identity. Common techniques are:
- OAuth: Lets people sign in using third-party services such as Google or Facebook.
- JWT (JSON Web Tokens): Offers a small and safe method to send data between entities.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Requiring a second kind of verification, it offers more security.
Protecting user data and preserving confidence depend on strong authentication and authorisation systems.
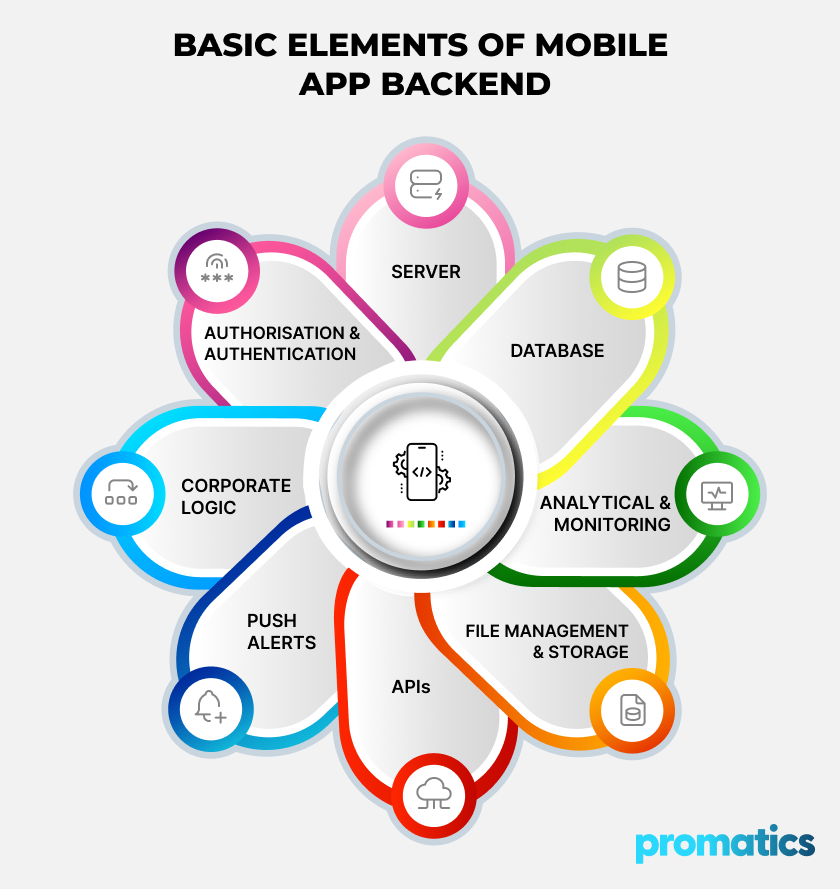
5. Corporate Logic
This specifies how data is generated, kept, and modified. It’s the set of guidelines guiding the app’s behaviour in different situations. For example, in an e-commerce application, business logic would govern how discounts are applied at checkout. Well-organised business logic guarantees consistency, dependability, and flexibility to evolving corporate needs.
6. File Management and Storage
Apps sometimes have to keep papers, videos, and photographs, among other files. Services such as Google Cloud Storage or AWS S3 guarantee rapid access and recovery by offering scalable options for file storage.
Efficient file management improves user experience by allowing quick loading times and consistent access to media content.
7. Push Alerts
Timely updates sent by push notifications keep users engaged. The delivery of these alerts is handled by backend services such as Apple Push Notification Service (APNS) or Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM).
By providing timely and relevant information, push notifications can be implemented properly and increase user retention and interaction.
8. Analytical and Monitoring
Tracking app performance and user interactions is essential. Tools such as New Relic, Datadog, or Prometheus help track metrics, find problems, and improve performance.
Comprehensive analytics let data-driven decision-making guide ongoing app improvement and refinement.
Mobile App Backend Solution Types
1. Service as a Software (SaaS)
SaaS offers ready-to-use backend systems that can be included in your application. Some illustrations are:
- AccuWeather API: Provides weather information for app integration.
- Shopify Headless Commerce: Uses Shopify’s backend but lets you create a bespoke front end.
- Contentful Headless CMS: Delivers and manages content across several platforms.
Advantages:
- Fast installation
- Lowered development expenses
Drawbacks:
- Minimal personalisation
- Reliance on outside companies
For apps with consistent backend needs, SaaS solutions are perfect since they allow for quick deployment and lower costs.
2. Mobile Backend as a Service (MBaaS)
MBaaS strikes a balance between SaaS and bespoke solutions. It offers pre-built backend parts with the option to include bespoke code. Among the well-known MBaaS systems:
- Firebase: Provides analytics, authentication, and real-time database.
- AWS Amplify: Offers a range of tools and services for creating scalable applications.
- Parse: A free backend system.
Advantages:
- Quicker creation
- Growth
Cons:
- Possible vendor lock-in
- For complicated applications, more customisation could be needed
MBaaS is appropriate for apps needing quick development and scalability without the burden of running backend infrastructure.
3. Tailor-Made Backend Systems
Building a custom backend from scratch provides total control for apps with particular needs. Applications requiring particular features, strong security, or complicated integrations will benefit from this strategy.
Advantages:
- Complete customisation
- Improved safety
Cons:
- Longer development time
- Increased expenses
For complicated applications where off-the-shelf solutions fall short, custom backend solutions are perfect since they offer tailored functionality and performance.
Tools and Technologies for Backend Development
1. Programming Languages
Selecting the right programming language is absolutely vital. Common selections are:
- JavaScript: Especially with Node.js, it is widely used.
- Python: Renowned for its simplicity and readability.
- Ruby: Provides fast development possibilities.
Project needs, team knowledge, and performance issues all influence the choice of language.
2. Frameworks
Frameworks offer a methodical basis for backend development. Among the most well-known frameworks are:
- Express.js: A simple and adaptable Node.js web application framework.
- Django: A high-level Python framework promoting fast development.
- Ruby on Rails: Written in Ruby, a server-side web application framework.
Choosing the right framework may guarantee maintainable, scalable codebases and speed development.
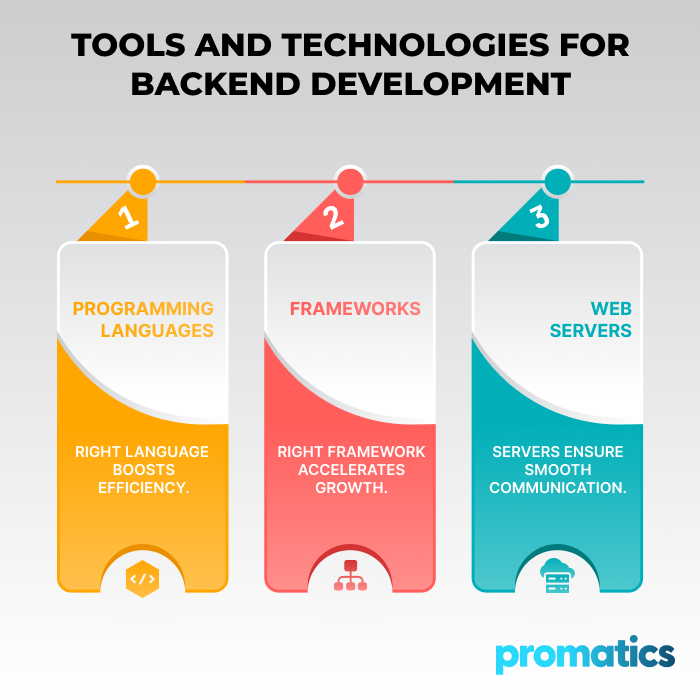
3. Web Servers
Acting as intermediaries handling HTTP requests from clients (mobile applications), web servers are essential in mobile app backend development since they provide suitable responses. They make sure the front end and back end communicate smoothly, effectively, and securely.
Web Server Functions in Mobile App Backends:
- Web servers handle incoming HTTP requests from mobile apps, process them, and send them to the suitable backend services or databases.
- Web servers return the suitable HTTP responses to the client after processing; these could be data retrieval, confirmation messages, or error alerts.
- In high traffic situations, web servers spread incoming requests over several backend servers to guarantee the best performance and avoid any one server from becoming a bottleneck.
- Web servers use security protocols like HTTPS to encrypt data transfer, therefore protecting sensitive information from possible attacks.
- They effectively deliver static assets, including JavaScript files, CSS files, and images, which are vital for the frontend of mobile apps.
Well-Liked Web Servers in Mobile App Backend Development:
- Apache Web Server: A popular open-source web server, Apache is well known for its adaptability and great module support. It can perform many tasks, from serving static material to functioning as a reverse proxy.
- Nginx: Known for its great performance and low resource use, Nginx is perfect for mobile apps with a big user base since it handles many connections exceptionally well.
- Microsoft Internet Information System (IIS): Developed by Microsoft, IIS is a strong web server that supports several protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and more, and fits perfectly with Windows environments.
Combining with Backend Frameworks:
Web servers usually process dynamic material in concert with backend frameworks. For example, if a mobile app asks for user data, the web server sends the request to a backend framework, such as Node.js or Django, which then communicates with the database to retrieve and provide the needed data.
Performance and Scalability Issues:
The backend infrastructure has to scale correspondingly as mobile apps become more popular. By letting several instances run concurrently, web servers enable horizontal scaling, therefore distributing the load and guaranteeing consistent performance. Web server-level caching systems also help to greatly lower server load and response times.
Best Security Practices:
The most important thing is to make sure the data sent between the mobile app and the backend is safe. By means of web servers:
- SSL/TLS Encryption: Encrypting data in transit to stop eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Firewalls: Establishing policies to prevent unauthorised access and possible attacks.
- Patches and Regular Updates: Updating the web server software to guard against acknowledged vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Web servers are essential to mobile app backend development since they guarantee efficient client-server communication, security maintenance, and scalability support. The performance and dependability of a mobile app can be greatly affected by the choice of web server and its proper configuration.
Should you require help with particular areas of mobile app backend development or have more questions, don’t hesitate to enquire!
Read more:- https://www.promaticsindia.com/blog/how-to-take-care-of-security-while-developing-mobile-apps

