How to Develop a Hyperlocal Delivery App: Your Comprehensive 2024 Guide

Table of Contents
- What is Hyperlocal commerce or Quick commerce?
- Hyperlocal Commerce in 2024: Current Trends and Insights
- An Overview of Business Models for Hyperlocal Delivery Apps
- Top Features to Include in Hyperlocal Delivery Apps
- User-Friendly Interface
- Location-Based Services
- Search and Filter Options
- Product and Service Listings
- User Reviews and Ratings
- Order Management
- Wallet and Payment Integration
- Loyalty Programs and Discount Offers
- Customer Support
- Vendor Management
- Real-Time Notifications
- Route Optimization for Delivery
- Analytics and Reporting
- Social Sharing
- Multi-Language and Multi-Currency Support
- Personalization
- In-App Chat
- Feedback Mechanism
- Integration with Other Services
- Booking and Scheduling
- Understanding Categories of Hyperlocal Delivery Apps
- Cost to build a Hyperlocal App
- Takeaway
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Hyperlocal commerce or Quick commerce?
Hyperlocal commerce refers to a business model that focuses on delivering goods and services within a limited geographic area, typically a neighbourhood or small community. This model leverages the proximity between suppliers and consumers to offer faster and more personalized service. Unlike traditional e-commerce, which can involve shipping products over long distances, hyperlocal commerce connects local vendors directly with nearby customers, often through online platforms or mobile apps. These platforms aggregate the offerings of various local businesses, such as grocery stores, pharmacies, restaurants, and service providers, enabling customers to browse and order from multiple sources in one place.
The primary distinction between hyperlocal commerce and last-mile delivery apps lies in their scope and operational focus. Last-mile delivery apps, such as those used by e-commerce giants like Amazon, concentrate on the final step of the delivery process, ensuring that products reach the customer from a central warehouse or distribution centre. These apps optimize logistics to cover the “last mile” of delivery efficiently, often using sophisticated algorithms and a network of couriers.
In contrast, quick commerce integrates the entire supply chain within a confined locality. It emphasizes sourcing from local businesses and aims to foster community ties by supporting small enterprises. This model can offer significant benefits, including quicker delivery times (often within an hour), reduced transportation costs, and a smaller carbon footprint due to the shorter distances involved. Additionally, hyperlocal platforms can cater to the unique preferences and needs of the local population, offering products and services that are more relevant and personalized.
Speed is king in hyperlocal commerce. Because partnered stores are situated nearby, deliveries can be fulfilled incredibly quickly, sometimes even within 10 minutes. This caters to those immediate needs – a forgotten ingredient for dinner or a birthday card at the last minute – that traditional e-commerce can’t always address.
While both hyperlocal commerce and last-mile delivery focus on prompt and efficient service, hyperlocal commerce differentiates itself by its commitment to locality, community engagement, and the sustainability of local economies. This model harnesses technology to bring traditional neighbourhood commerce into the digital age, creating a seamless bridge between consumers and local businesses.
Hyperlocal Commerce in 2024: Current Trends and Insights
Hyperlocal commerce has experienced significant growth across the globe, driven by the increasing demand for convenience and the rise of digital platforms that connect consumers with local vendors. This model has seen substantial traction in the USA, Europe, and Asia, particularly in India, each with unique market dynamics and leading players.
In the United States, hyperlocal commerce is thriving, with several key players dominating the market. Instacart, a major grocery delivery service, saw a surge in demand during the COVID-19 pandemic. The most popular hyperlocal app in USA that is Instacart is likely to cross $4 Billion in revenue by then end of 2024. They boast and impressive user base of over 10 million active users. DoorDash, primarily known for food delivery, expanded its services to include grocery and convenience store items. In 2023, DoorDash generated over $8.6 billion in revenue, holding a 57% market share in the food delivery sector. Another notable player, Postmates (acquired by Uber), continues to be a significant contributor to hyperlocal delivery, offering diverse services from groceries to household items.
In Europe, hyperlocal commerce is also burgeoning, with companies like Deliveroo and Glovo leading the charge. Deliveroo, operating in several European countries, reported a revenue of over £2 billion in 2023, serving millions of customers with quick deliveries from local restaurants and stores. Glovo, based in Spain, expanded rapidly across Southern and Eastern Europe, offering services from food delivery to groceries and pharmacy items. In 2023, Glovo’s revenue surpassed €700 million, with millions of active users across 25 countries. These platforms have invested heavily in technology and logistics to ensure swift and reliable service. France boasts companies like Carrefour Livraison, leveraging its supermarket network for hyperlocal deliveries. Customer numbers are steadily rising across the continent, driven by convenience and a growing comfort level with online ordering.
Asia presents a diverse and rapidly expanding market for quick commerce. In India, companies like Swiggy and Dunzo are at the forefront. Swiggy, initially a food delivery service, diversified into grocery and household item deliveries through Swiggy Genie. In 2024, Swiggy’s revenue will cross $1 billion, with over 20 million active users. Dunzo, another prominent player, specializes in quick deliveries of groceries, medicines, and other essentials, with a revenue of $60 million in 2023 and over 3 million users.
A crucial aspect of hyperlocal commerce is the role of hyperlocal enablers—companies that facilitate rapid and efficient deliveries. These enablers include logistics providers and technology platforms that optimize delivery routes and manage local fleets of couriers. Companies like Shadowfax and Delhivery in India, Stuart in Europe, and Roadie and Gopuff in the USA play pivotal roles. Shadowfax, for instance, partners with various hyperlocal platforms, ensuring swift deliveries within cities and towns. As of 2024, Shadowfax managed over 1.5 million deliveries per day.
Growth and Future Prospects
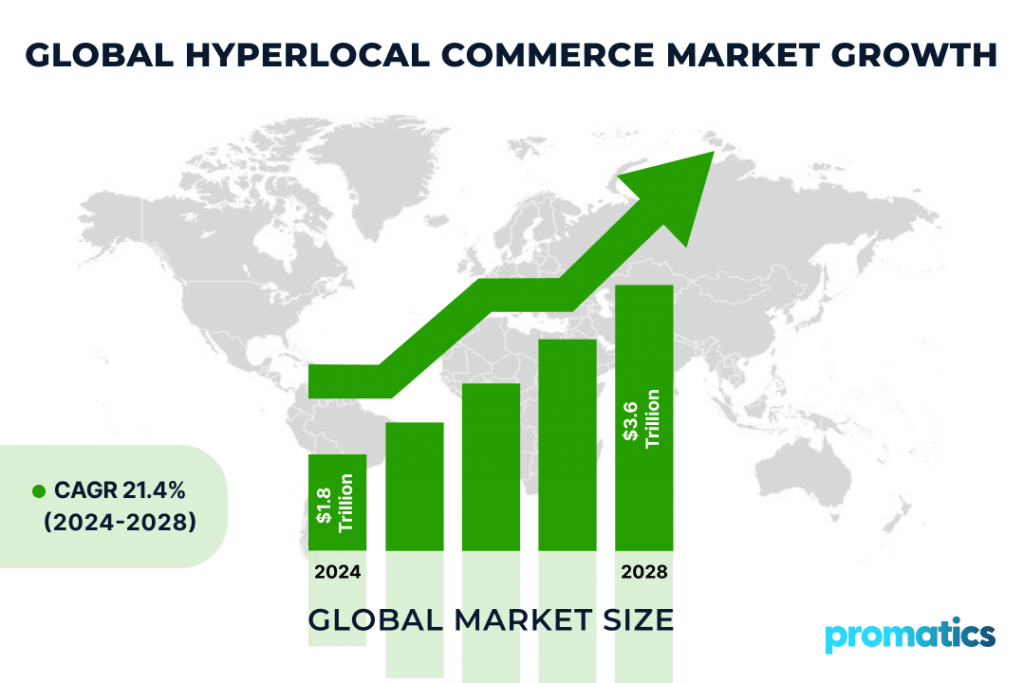
The hyperlocal commerce market continues to grow robustly. In 2024, the global market size was valued at approximately $1.8 trillion, with projections to reach $3.6 trillion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 21.4%. This growth is driven by increasing urbanization, smartphone penetration, and a shift towards online shopping. Companies are continually innovating to enhance user experience, investing in AI and machine learning to improve delivery efficiencies and customer satisfaction.
With substantial revenue figures, a growing customer base, and robust support from logistics enablers, this sector is poised for continued expansion and innovation globally.
An Overview of Business Models for Hyperlocal Delivery Apps
Hyperlocal apps operate under various business models, each tailored to meet the needs of their specific market and customer base. Here are some of the most prevalent business models in hyperlocal commerce:
1.Marketplace Model
The marketplace model involves creating a platform that connects local vendors with consumers. The app acts as an intermediary, facilitating transactions without owning the inventory. Examples include food delivery services like Uber Eats and Grubhub.
In this model, the app aggregates offerings from multiple vendors, providing users with a wide range of choices in one place. Vendors benefit from increased visibility and access to a larger customer base, while consumers enjoy the convenience of browsing and ordering from various local businesses. The app typically earns revenue through commissions on each transaction, service fees, or subscription fees from vendors. This model relies heavily on building a robust network of local partners and maintaining high service quality to retain customers and vendors alike.
2.On-Demand Delivery Model
The on-demand delivery model focuses on quick, often same-day delivery of goods and services. This model is prevalent in grocery delivery apps like Instacart and BigBasket. The key differentiator here is speed and convenience, catering to customers who need items urgently.
In this model, the app coordinates with local stores and a fleet of delivery personnel to ensure rapid fulfillment of orders. The revenue is generated through delivery fees, service charges, and sometimes through partnerships with local businesses. To succeed, companies need efficient logistics, a well-managed inventory system, and a reliable network of delivery drivers. This model requires significant investment in technology and infrastructure to optimize delivery routes and manage high volumes of orders seamlessly.
3. Subscription-Based Model
Some hyperlocal apps operate on a subscription-based model, offering users premium services for a recurring fee. Here customers pay a membership fee for access to faster delivery services and exclusive deals.
This model provides a steady revenue stream and fosters customer loyalty by offering consistent value through perks like free delivery, special discounts, and early access to products. Subscribers are often more engaged and spend more over time compared to non-subscribers. To attract and retain subscribers, apps must continuously enhance their offerings and ensure a high level of service. The challenge lies in balancing the cost of providing premium services with the subscription fees charged to customers.
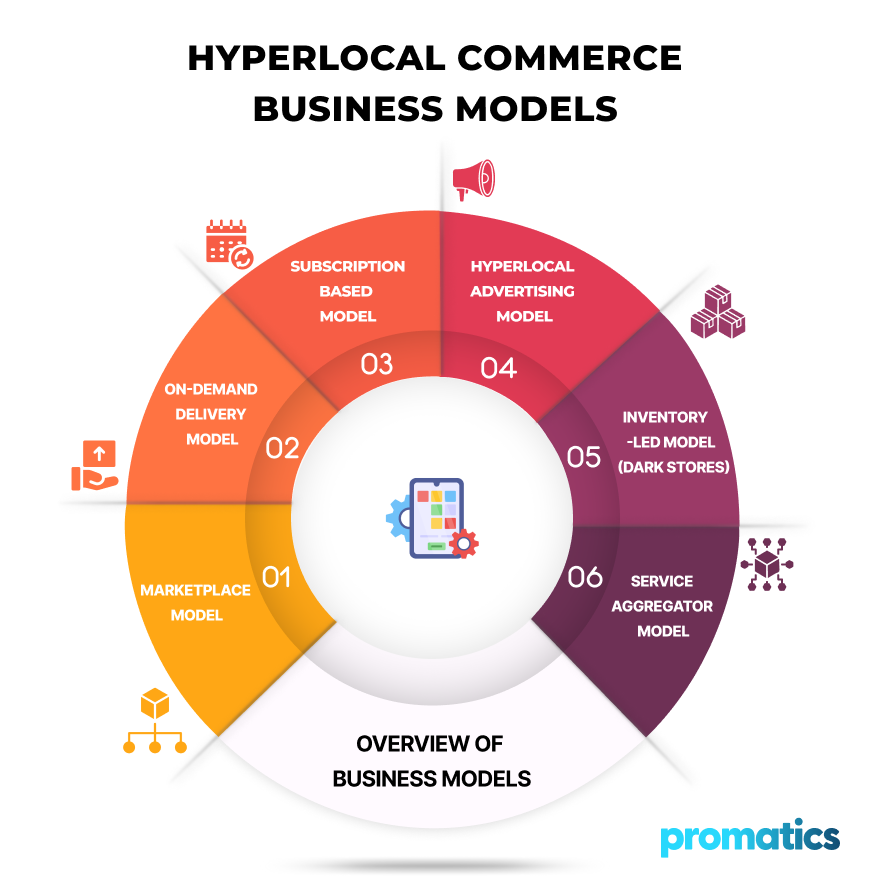
4. Hyperlocal Advertising Model
In this model, hyperlocal apps generate revenue through targeted advertising, leveraging their platform to promote local businesses to nearby consumers. Apps like Yelp and Foursquare utilize this approach, providing businesses with advertising opportunities based on user location and preferences.
This model capitalizes on the local nature of hyperlocal commerce, offering advertisers highly relevant and targeted audiences. Businesses pay for ads, featured listings, and promotional placements within the app. This can significantly enhance their visibility and drive foot traffic. The app needs to maintain a large and active user base to attract advertisers and must invest in robust data analytics to offer precise targeting. User experience should remain a priority, ensuring that ads are relevant and non-intrusive.
5. Inventory-Led Model (Dark Stores)
Unlike the marketplace model, the inventory-led model involves the app owning and managing its inventory. Examples include Zepto and Blinkit (formerly Grofers) in India, which stocks goods in its warehouses and fulfills orders directly.
This model allows for greater control over the supply chain, inventory management, and pricing. It can ensure faster delivery times and higher product availability. Revenue is generated through product sales, and profits are influenced by efficient inventory turnover and supply chain management. However, this model requires significant upfront investment in warehousing and logistics. It also entails higher risks associated with inventory management, such as overstocking or understocking.
6. Service Aggregator Model
The service aggregator model focuses on aggregating local services rather than goods. Apps like UrbanCompany in India offer a platform where users can book various local services such as home cleaning, repairs, and beauty treatments.
Revenue is earned through commissions on each service booked, subscription fees from service providers for premium listings, or advertising. This model benefits from the increasing demand for convenience in accessing local services. Key to its success is building a comprehensive network of reliable service providers and ensuring high service standards. Quality control and customer satisfaction are critical, as the app’s reputation directly impacts its ability to attract and retain users and service partners.
Top Features to Include in Hyperlocal Delivery Apps
Hyperlocal apps come with a range of features designed to facilitate seamless interactions between local businesses and customers. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the essential features commonly found in hyperlocal apps:
1. User-Friendly Interface
A clean, intuitive user interface (UI) is crucial for ensuring that users can navigate the app effortlessly. This includes a well-organized layout, clear navigation menus, and easy-to-use icons and buttons. The design should cater to both tech-savvy users and those less familiar with mobile apps.
2. Location-Based Services
Hyperlocal apps leverage GPS and other location-based technologies to connect users with nearby vendors. This feature allows the app to provide personalized recommendations based on the user’s location and to display only the relevant businesses and services in the vicinity.
3. Search and Filter Options
A powerful search function helps users find specific products, services, or businesses quickly. Filters allow users to narrow down their search based on criteria like price, distance, ratings, and categories, enhancing the overall user experience.
4. Product and Service Listings
Comprehensive listings provide detailed information about available products and services. This includes descriptions, prices, images, and other relevant details. These listings help users make informed decisions by providing all the necessary information in one place.
5.User Reviews and Ratings
User-generated reviews and ratings are vital for building trust and credibility. This feature allows customers to share their experiences, helping others make informed choices. It also encourages businesses to maintain high standards of quality and service.
6. Order Management
Efficient order management systems handle the entire process from order placement to delivery. This includes order tracking, status updates, and notifications. Users can view their order history, track current orders in real-time, and receive notifications about their order status.
7. Wallet and Payment Integration
Multiple payment options provide users with flexibility and convenience. Integration with various payment gateways supports credit/debit cards, digital wallets, and net banking. Secure payment processing ensures that transactions are safe and user data is protected.
8. Loyalty Programs and Discount Offers
Loyalty programs and special offers incentivize repeat usage. Features like reward points, discount coupons, and exclusive deals can be integrated into the app to encourage customer loyalty and increase engagement.
9. Customer Support
Reliable customer support is essential for addressing user queries and issues promptly. This can include live chat, email support, and a comprehensive FAQ section. Effective customer support enhances user satisfaction and helps build long-term relationships with customers.
10. Vendor Management
Vendor management tools help businesses manage their profiles, inventory, orders, and customer interactions. This feature enables vendors to update their listings, track orders, and respond to customer reviews, ensuring smooth operations and high service quality.

11. Real-Time Notifications
Push notifications keep users informed about their orders, special offers, and updates from their favorite businesses. This feature enhances user engagement by providing timely and relevant information directly to their devices.
12. Route Optimization for Delivery
For apps offering delivery services, route optimization is crucial for ensuring timely deliveries. This feature uses algorithms to determine the most efficient delivery routes, reducing delivery times and operational costs.
13. Analytics and Reporting
Analytics and reporting tools provide valuable insights into user behavior, sales trends, and operational performance. Businesses can use this data to make informed decisions, optimize their offerings, and improve overall efficiency.
14. Social Sharing
Social sharing features allow users to share their experiences, favorite products, or special deals with their friends and family on social media platforms. This can help drive word-of-mouth marketing and increase the app’s visibility.
15. Multi-Language and Multi-Currency Support
To cater to diverse user bases, hyperlocal apps often include multi-language and multi-currency support. This feature makes the app accessible to users from different linguistic and economic backgrounds, enhancing user experience and expanding the app’s reach.
16. Personalization
Personalization features customize the user experience based on individual preferences and behaviors. This can include personalized recommendations, targeted offers, and customized content, which helps in increasing user engagement and satisfaction.
17. In-App Chat
In-app chat allows users to communicate directly with vendors or customer support. This feature can help clarify queries, negotiate prices, and provide real-time assistance, enhancing the overall customer experience.
18. Feedback Mechanism
A feedback mechanism enables users to provide suggestions and report issues. This feature is crucial for continuous improvement, as it helps developers and businesses understand user needs and address any problems promptly.
19. Integration with Other Services
Integration with third-party services like Google Maps, payment gateways, and social media platforms enhances the functionality of hyperlocal apps. These integrations streamline operations and improve the overall user experience by adding more value to the core services of the app.
20. Booking and Scheduling
For apps offering services like home repairs, beauty treatments, or fitness sessions, a booking and scheduling feature is essential. This allows users to select preferred dates and times, and service providers can manage their appointments efficiently.
Understanding Categories of Hyperlocal Delivery Apps
Hyperlocal apps cater to various needs within specific geographic areas, providing a range of services and products. Here are the different types of hyperlocal apps, each designed to serve a particular market niche:
1. Food Delivery Apps
Food delivery apps connect local restaurants with customers who want meals delivered to their doorstep. Examples include Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Zomato. These apps offer a wide range of cuisines from nearby eateries, allowing users to browse menus, place orders, and track deliveries in real-time.
Food delivery apps typically generate revenue through delivery fees, service charges, and commissions from restaurants. They focus on providing a seamless user experience with features like easy payment options, customizable orders, and reliable customer service. To ensure quick deliveries, these apps maintain a robust logistics network, often employing a large number of delivery drivers. The success of these apps depends on their ability to offer a diverse selection of restaurants, maintain high service standards, and manage delivery logistics efficiently.
2. Grocery Delivery Apps
Grocery delivery apps allow users to order groceries and household essentials from local stores. Examples include Instacart, BigBasket, and Amazon Fresh. These apps provide the convenience of shopping from home, offering a wide selection of products, including fresh produce, dairy, and pantry staples.
Revenue for grocery delivery apps comes from delivery fees, service charges, and partnerships with local retailers. They prioritize speed and reliability, often offering same-day or next-day delivery options. These apps use sophisticated inventory management systems to ensure product availability and freshness. They also employ a network of shoppers and delivery personnel to fulfill orders promptly. The key to their success lies in maintaining a large inventory, providing competitive prices, and ensuring customer satisfaction through timely and accurate deliveries.
3. Pharmacy Delivery Apps
Pharmacy delivery apps cater to the need for quick and convenient access to medications and health-related products. Examples include 1mg (India), Capsule (USA), and LloydsDirect (UK). These apps enable users to upload prescriptions, consult with pharmacists, and order medicines online.
Revenue is generated through delivery fees, service charges, and margins on pharmaceutical products. These apps focus on ensuring the authenticity and quality of medicines, often partnering with licensed pharmacies. They provide added services such as health consultations, lab tests, and wellness products. The success of pharmacy delivery apps hinges on their ability to offer a wide range of medicines, ensure timely deliveries, and maintain stringent quality control measures. They also prioritize user privacy and data security, given the sensitive nature of health information.
4. Home Services Apps
Home services apps connect users with local service providers for various household needs, such as cleaning, repairs, beauty treatments, and more. Examples include Urban Company (formerly UrbanClap) in India, Handy in the USA, and TaskRabbit in multiple countries. These apps offer a platform for booking services, managing appointments, and making payments.
Revenue is typically earned through commissions on each service booked, subscription fees from service providers, and advertising. Home services apps focus on building a reliable network of vetted professionals, ensuring quality and safety. They provide user reviews and ratings to help customers choose the best service providers. The key to their success is maintaining high service standards, offering a wide range of services, and ensuring customer satisfaction through reliable and professional service delivery.
5. Logistics and Courier Apps
Logistics and courier apps or uber for trucking provide on-demand delivery services for packages and documents within a local area. Examples include Postmates (USA), Dunzo (India), and Stuart (Europe). These apps cater to both individuals and businesses needing quick and reliable delivery solutions.
Revenue is generated through delivery fees, service charges, and partnerships with businesses. Logistics apps focus on optimizing delivery routes, ensuring timely deliveries, and providing real-time tracking. They employ a network of couriers who can pick up and deliver items within hours. The success of these apps depends on their ability to manage logistics efficiently, offer competitive pricing, and ensure the safe and timely delivery of packages. They also invest in technology to improve route planning and enhance user experience.
6. Hyperlocal News and Information Apps
Hyperlocal news and information apps provide localized news, events, and information relevant to a specific community or neighborhood. Examples include Nextdoor (USA), Presshop (UK), and Public (India). These apps keep residents informed about local happenings, services, and opportunities.
Revenue is typically earned through advertising, sponsored content, and partnerships with local businesses. These apps focus on building a strong community presence, offering timely and relevant information. They often include features like community forums, event calendars, and classifieds. The success of hyperlocal news apps depends on their ability to provide accurate and engaging content, foster community engagement, and attract local advertisers. They play a crucial role in connecting residents and promoting local businesses and events.
Cost to build a Hyperlocal App
Building a hyperlocal app involves multiple stages and resources, from planning and design to development, testing, and deployment. The costs can vary significantly between the US and India due to differences in labor rates, infrastructure, and other factors. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the specifics and a cost comparison between the two countries, followed by a suggested team structure.
Key Components of a Hyperlocal App Development Project
- Planning and Requirement Analysis
- Design
- UI/UX Design
- Development
- Frontend Development
- Backend Development
- API Integration
- Testing
- Quality Assurance (QA) Testing
- Deployment and Maintenance
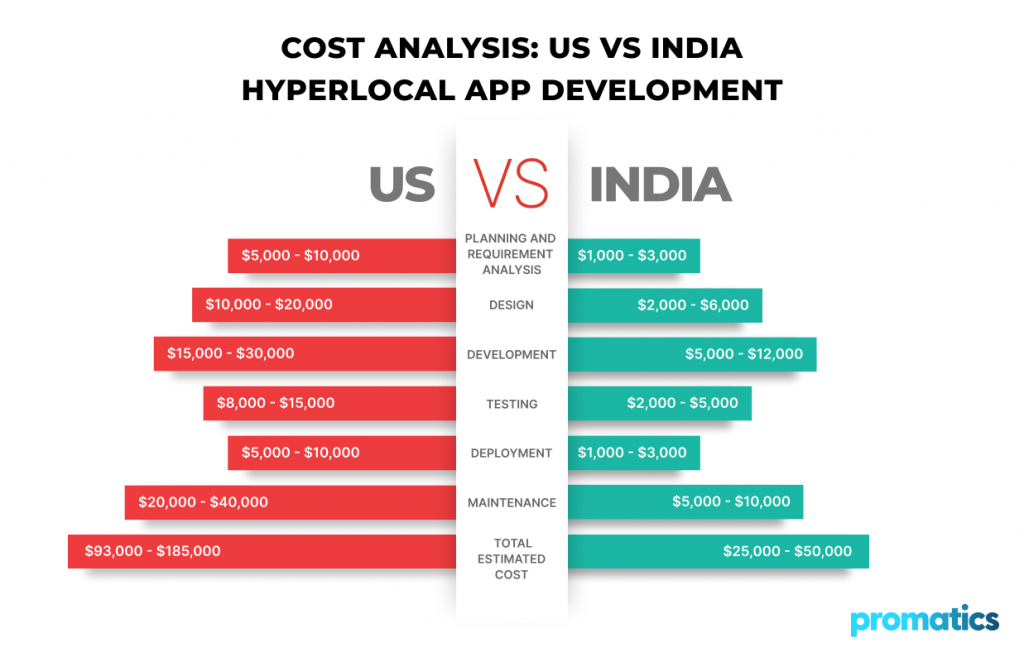
Cost Breakdown in the US and India
- Planning and Requirement Analysis
- US: $5,000 – $10,000
- India: $1,000 – $3,000
- Design
- UI/UX Design:
- US: $10,000 – $20,000
- India: $2,000 – $6,000
- UI/UX Design:
- Development
- Frontend Development:
- US: $15,000 – $30,000
- India: $5,000 – $12,000
- Backend Development:
- US: $20,000 – $40,000
- India: $8,000 – $15,000
- API Integration:
- US: $10,000 – $20,000
- India: $3,000 – $6,000
- Frontend Development:
- Testing
- Quality Assurance (QA):
- US: $8,000 – $15,000
- India: $2,000 – $5,000
- Quality Assurance (QA):
- Deployment and Maintenance
- Deployment:
- US: $5,000 – $10,000
- India: $1,000 – $3,000
- Deployment:
- Maintenance (Annual):
- US: $20,000 – $40,000
- India: $5,000 – $10,000
Total Estimated Cost
- US: $93,000 – $185,000
- India: $25,000 – $50,000
Suggested Team Structure
- Project Manager
- Oversees the project, coordinates between teams, ensures timelines and budgets are met.
- Business Analyst
- Gathers requirements, creates documentation, ensures the app meets business objectives.
- UI/UX Designer
- Designs the user interface and user experience, creates wireframes and prototypes.
- Frontend Developers (2-3)
- Builds the client-side of the application, ensures responsiveness and functionality.
- Backend Developers (2-3)
- Oversees the project, coordinates between teams, ensures timelines and budgets are met.
- QA Testers (2-3)
- Conducts various tests to ensure the app is bug-free and performs well.
- DevOps Engineer
- Manages deployment, continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, and server management.
- Mobile App Developer (iOS and Android)
- Specializes in developing and optimizing the app for mobile platforms.
- Marketing Specialist
- Develops marketing strategies, manages promotions, and works on user acquisition and retention.
Cost Analysis: Developing a Hyperlocal App in the US vs. India
The significant cost difference between developing a hyperlocal app in the US versus India primarily stems from labor costs. In the US, developers, designers, and other professionals command higher salaries due to the higher cost of living and demand for tech talent. Conversely, in India, labor costs are significantly lower while maintaining a high level of expertise, making it a popular destination for outsourcing app development.
- Planning and Requirement Analysis: The cost in the US is 5-10 times higher than in India.
- Design: UI/UX design costs in the US are around 3-5 times higher.
- Development: Frontend, backend, and API integration costs are approximately 2-4 times higher in the US.
- Testing: QA testing in the US costs about 4-6 times more.
- Deployment and Maintenance: Deployment costs are about 5-10 times higher, and maintenance costs are around 4-8 times higher in the US.
Developing a hyperlocal app in the US is significantly more expensive than in India, mainly due to higher labour costs. Companies looking to minimize expenses without compromising on quality often choose to outsource to India, where they can leverage skilled professionals at a fraction of the cost. The suggested team structure provides a comprehensive approach to cover all aspects of app development, ensuring a high-quality product regardless of the location.
Takeaway
The hyperlocal commerce sector is on an upward trajectory, presenting lucrative opportunities for businesses and developers alike. As consumer preferences shift towards convenience and immediacy, quick commerce apps have become integral in facilitating seamless connections between local vendors and their customers.
The significant cost difference in developing hyperlocal apps between the US and India highlights the strategic advantage of outsourcing, enabling businesses to optimize their budgets while leveraging high-quality talent. This cost efficiency, coupled with a well-structured and competent team, can drive the successful implementation of hyperlocal solutions.
Ultimately, the future of hyperlocal commerce hinges on innovation, adaptability, and the ability to cater to hyper-specific consumer demands. Businesses that prioritize these aspects will be well-positioned to thrive in this dynamic market, offering unparalleled value and convenience to their local communities.
FAQs
Q1. Which Company Offers the Best Hyperlocal App Development Services?
Determining the best company for hyperlocal app development depends on various factors such as expertise, portfolio, client reviews, and industry experience. Having said that Promatics Technologies stands out as a top choice for hyperlocal app development services. With focus on On Demand custom app development Promatics leverages the latest technologies to meet the unique demands of hyperlocal services.
One of the key reasons for their prominence is their extensive portfolio, which includes successful hyperlocal apps across various sectors such as food delivery, grocery shopping, and on-demand services. This diverse experience equips them with the insights needed to tackle different challenges in hyperlocal commerce effectively. Furthermore, Promatics emphasizes a robust post-launch support system, helping clients with maintenance and updates, which is crucial for the dynamic nature of hyperlocal services.
Q2. Which is the Best Tech Stack to Develop a Hyperlocal Delivery App?
Choosing the right tech stack for developing a hyperlocal delivery app is crucial for performance and scalability. A popular combination includes React Native or Flutter for mobile app development, enabling cross-platform functionality. For the backend, Node.jsor Djangoare excellent choices, providing robust frameworks to handle real-time data and API management. For database management, MongoDBor PostgreSQLcan effectively manage user and order data. Additionally, integrating Firebase can enhance real-time notifications and user authentication. Cloud services like AWS or Google Cloud ensure scalable hosting and storage solutions. Ultimately, the best tech stack balances functionality, development speed, and scalability, catering to the unique demands of hyperlocal services.
Q3. What Is the Estimated Cost of Developing a Hyperlocal App?
The cost of developing a hyperlocal app can vary widely based on factors like complexity, features, and the development team’s location. In general, the estimated cost ranges from $25,000 to $50,000. For a basic app with essential features like user registration, location tracking, and payment integration, you might spend around $20,000 to $25,000. A more complex app that includes advanced functionalities such as real-time chat, analytics, and multiple user roles could range from $40,000 to $50,000. Additionally, ongoing maintenance and updates should also be factored into your budget, typically costing 15-20% of the initial development cost annually.
Q4. What Should I Consider When Hiring a Developer for a Hyperlocal App?
When hiring a developer for a hyperlocal app, consider several key factors. First, evaluate their technical expertise in relevant programming languages and frameworks essential for your app. Review their portfolio to assess previous projects, especially those related to hyperlocal services. Client testimonials and case studies provide insight into their reliability and communication skills. Additionally, consider their understanding of the hyperlocal market and user experience design, as these are crucial for the app’s success. It’s also important to discuss project timelines, budget, and post-launch support. Lastly, ensure they are adaptable and open to feedback, as collaboration is vital in achieving your project goals.
